The 4 biggest disadvantages of data virtualization
In the midst of the data (r)evolution, the allure of data and database virtualization has led many customers to explore new ways of combining test data management with this technology. However, in our quest to provide the best solutions to our valued customers, we feel it’s crucial to shed light on the less-discussed side of the coin – the disadvantages of data virtualization.
In this blog post, we aim to offer a comprehensive perspective to help you make informed decisions. While we wholeheartedly advocate the use of the solutions we provide, we also acknowledge that not every approach suits every industry or user. Join us as we delve into the essential factors and considerations that deserve your attention.
1. Limited Data Manageability with VDBs
While virtual databases (VDBs) promise efficiency gains in setting up test environments, they often fall short in the crucial task of data management. Despite initial time savings, a significant portion of resources is still consumed in locating and preparing test data. This challenge is exacerbated when dealing with vast databases containing millions, or even billions, of records.
Recent research underscores this issue, revealing that a staggering 46% of our time in data-related tasks is dedicated to analytics, data searching, and test data preparation. In many standard business scenarios, the common practice involves creating a 100% copy of the production database and distributing it to various teams via VDBs. This approach, while expedient, may not address the core issues associated with data manageability.
2. Vulnerability to Single Point of Failure
One of the often-overlooked drawbacks of data virtualization is the susceptibility to a single point of failure. Imagine a scenario where the server, or the central component of your data virtualization infrastructure, experiences downtime. When this happens, it has a cascading effect on all virtual databases (VDBs) hosted on the platform.
In essence, your reliance on a centralized virtualization infrastructure means that there are limited fallback options when issues arise, posing a substantial risk to the timely delivery of your products and services. Mitigating this risk requires careful consideration and potentially redundant systems to ensure uninterrupted data access and operational continuity.
3. Performance Challenges
When it comes to running large batch processes on a data virtualization server, performance can quickly become a significant concern. While data virtualization excels in providing a unified view of data from various sources, it may struggle to keep pace with the demands of resource-intensive tasks, particularly when dealing with extensive databases.
To mitigate these performance challenges, organizations may need to invest in powerful hardware or explore alternative/additional test data management strategies (like data subsetting) that are better suited for resource-intensive tasks.
4. Limited Virtualization Scope
A critical limitation of data virtualization lies in its technology-dependent nature. It’s essential to recognize that not every aspect of your data ecosystem can be effectively virtualized. While data virtualization can serve as a valuable partial solution for certain challenges, attempting to construct an entire Test Data Management (TDM) architecture solely through virtualization may prove impractical and insufficient.
Virtualization works most effectively when dealing with specific data integration and access scenarios. However, certain components and processes within your TDM architecture may resist virtualization due to various technical, security, or compatibility constraints.
Attempting to force the entire TDM infrastructure into a virtualization framework could result in compromises and inefficiencies. Some data sources or legacy systems may not readily support virtualization, and in such cases, attempting to do so might introduce complexities that outweigh the benefits.
A well-rounded TDM strategy should consider a blend of virtualization alongside other test data management techniques, such as data masking, subsetting, or provisioning. This holistic approach ensures that all aspects of your TDM architecture are adequately addressed, striking a balance between flexibility and practicality.
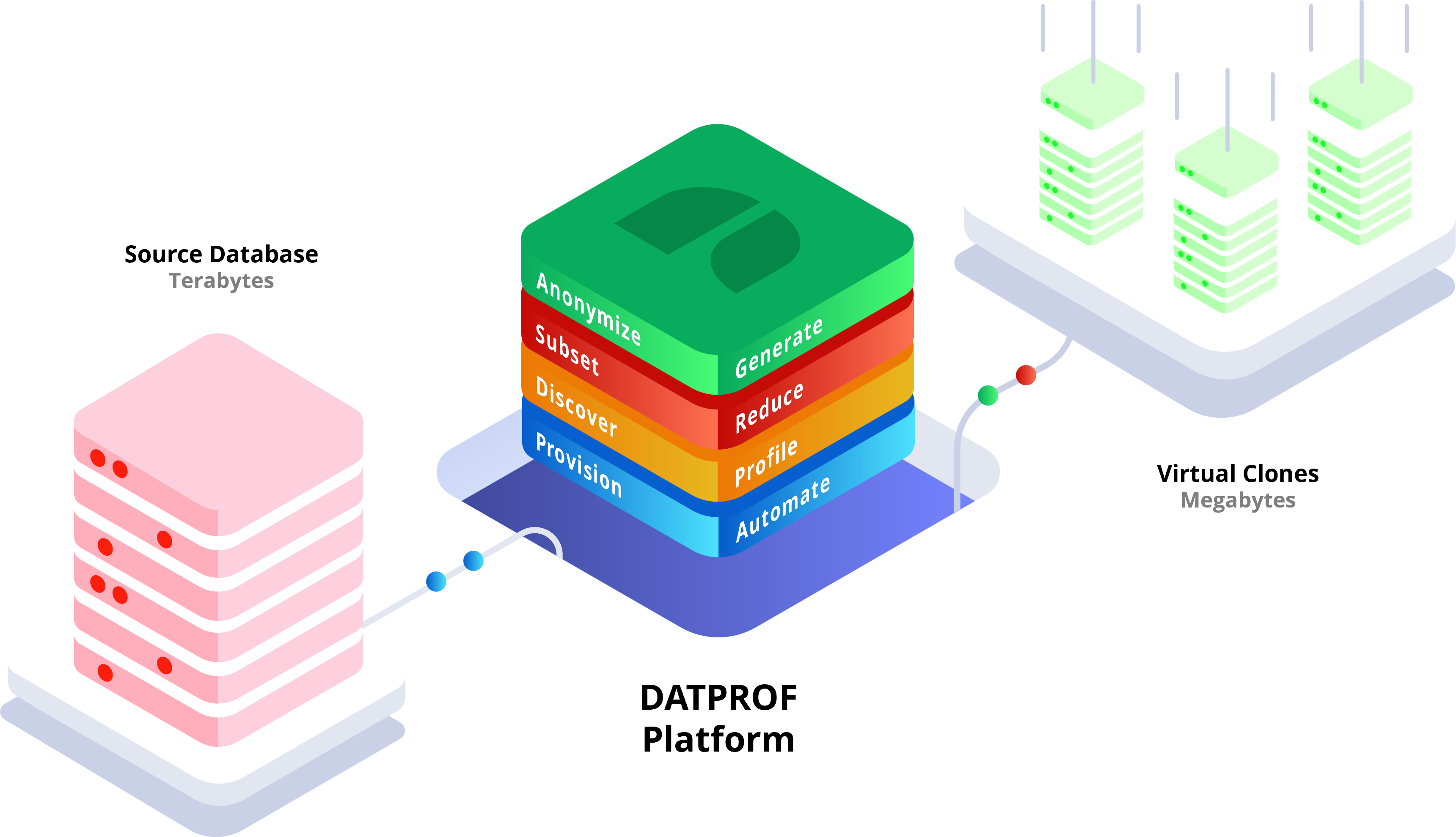
DATPROF Virtualize – Elevating Your TDM Strategy
Throughout our exploration of the advantages and disadvantages of data virtualization, one solution has consistently stood out as a game-changer: DATPROF Virtualize. In the realm of Test Data Management (TDM), DATPROF Virtualize shines as a remarkable addition that transforms challenges into opportunities, while offering unique benefits to organizations seeking a more efficient and flexible data management strategy.
Holistic Test Data Management
DATPROF Virtualize is not a solution for all your test data challenges. It complements your TDM strategy by offering seamless integration with other test data management techniques. This synergy allows for a comprehensive approach, where virtualization, data masking, subsetting, and provisioning work together harmoniously to meet diverse data needs.
Incorporating DATPROF Virtualize into your Test Data Management strategy unlocks a world of possibilities. It empowers your organization to not only overcome the challenges associated with data virtualization but also leverage its advantages to deliver superior products and services with greater efficiency. With DATPROF Virtualize, your TDM strategy takes a giant leap forward, positioning your organization at the forefront of modern data management practices.
Book a meeting
Schedule a product demonstration with one of our TDM experts
FAQ
What is data virtualization?
Data virtualization is an approach that can create and distribute virtual copies of data for different goals. The data itself is not copied; only changes in the data are saved.
What is the greatest advantage of data virtualization?
The data itself is not copied; only changes in the data are saved. This way hardware and infrastructure costs can be saved.
What is the greatest disadvantage of data virtualization?
A disadvantage of data virtualization is often the complexity of the implementation and still using all of the data instead of only the relevant data.